Understanding PubMed: A Comprehensive Guide
PubMed, a treasure trove of biomedical literature, is an invaluable resource for researchers, healthcare professionals, and students alike. In this detailed guide, we’ll explore the ins and outs of PubMed, helping you navigate its vast database with ease.
What is PubMed?
PubMed is a free search engine for biomedical literature, including life science journals. Developed by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) at the National Library of Medicine (NLM), PubMed provides access to over 32 million citations from biomedical literature. It includes links to full-text articles and other related resources.
How to Access PubMed
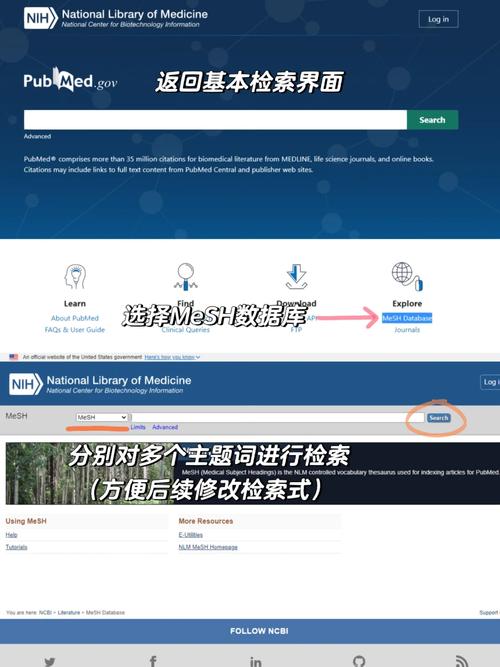
Accessing PubMed is straightforward. Simply visit pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov in your web browser. Once on the homepage, you’ll find a search box where you can enter your query.
Searching PubMed
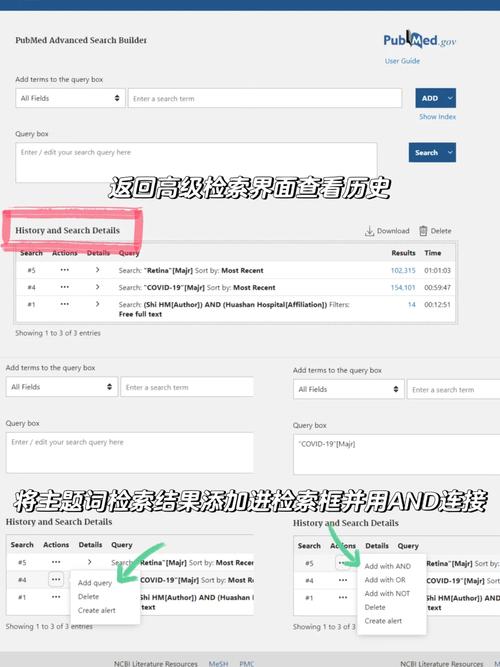
When searching PubMed, you can use keywords, author names, journal titles, or a combination of these. For example, if you’re looking for articles on “cancer treatment,” simply type that phrase into the search box and press Enter.
PubMed offers advanced search options, allowing you to refine your search further. You can limit your search to specific types of articles, such as clinical trials or reviews, and filter results by publication date, language, and more.
Understanding Search Results
After performing a search, you’ll be presented with a list of search results. Each entry includes the title of the article, the authors, the journal in which it was published, and the publication date. You can also view the abstract of the article, which provides a summary of the study’s findings.
Sorting and filtering your search results can help you find the most relevant articles. You can sort by relevance, publication date, or other criteria. Additionally, you can filter results by article type, language, and more.
Accessing Full-Text Articles
While PubMed provides access to abstracts and citations, it doesn’t always offer full-text articles. However, PubMed often includes links to full-text articles available through other sources, such as the journal’s website or a university library.
When viewing an article’s abstract, look for a link to the full text. If the article is available online, you may be able to access it for free. If not, you may need to purchase the article or request it through interlibrary loan.
Using PubMed’s Advanced Features
PubMed offers several advanced features to enhance your search experience. Here are a few highlights:
-
My NCBI: Create a personal account to save searches, organize citations, and receive email alerts when new articles are published on your topics of interest.
-
Related Articles: View a list of articles related to the one you’re reading, helping you explore the topic further.
-
MeSH Browser: Navigate the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) database to find the best search terms for your topic.
-
Journal Browser: Explore the contents of specific journals and find articles of interest.
Table: PubMed’s Key Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Free Access | PubMed is a free resource, providing access to millions of biomedical literature citations. |
| Comprehensive Database | PubMed includes citations from over 32 million biomedical literature sources. |
| Advanced Search Options | Refine your search using keywords, author names, journal titles, and more. |
| Full-Text Links | Access full-text articles when available, or find alternative sources for articles not available through PubMed. |
| Personalized Account | Create a My NCBI account to save searches, organize citations, and receive email alerts. |
Conclusion
PubMed is an
