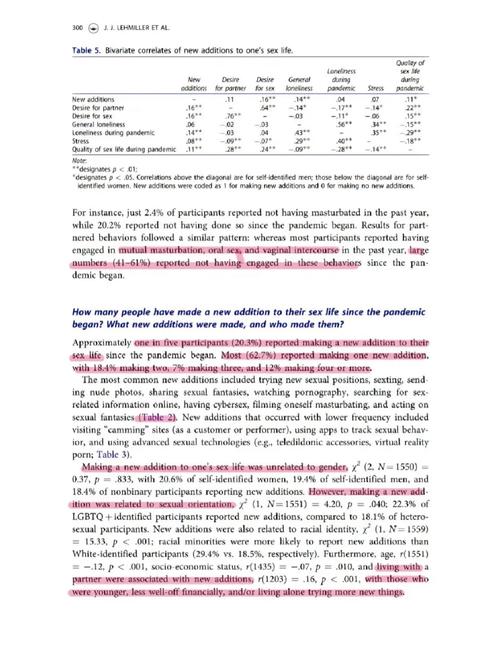
Understanding OMS Disease Life Expectancy: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to OMS disease, life expectancy is a topic of great concern for both patients and their families. OMS, or Osteosarcoma, is a type of bone cancer that can affect individuals of any age, though it is most commonly diagnosed in children and adolescents. In this article, we delve into the various aspects of OMS disease life expectancy, providing you with a detailed and multi-dimensional overview.
What is Osteosarcoma?
Osteosarcoma is a malignant tumor that originates in the bone. It is the most common primary bone cancer in children and adolescents, with a higher incidence in males than females. The cancer typically arises in the long bones, such as the arms and legs, but can also occur in the spine, pelvis, or skull.

Life Expectancy Statistics
Life expectancy for individuals with OMS disease can vary widely depending on several factors, including the stage of the cancer at diagnosis, the age of the patient, and the response to treatment. According to the American Cancer Society, the five-year survival rate for osteosarcoma is approximately 70% for patients diagnosed before the age of 40.
However, this figure can be broken down further. For patients diagnosed at a younger age, the five-year survival rate is around 80%. In contrast, for patients diagnosed at an older age, the survival rate is lower, around 50%. It is important to note that these statistics are general estimates and may not reflect the individual prognosis of every patient.
Factors Influencing Life Expectancy
Several factors can influence the life expectancy of individuals with OMS disease:
-
Stage of Cancer: The stage of the cancer at diagnosis plays a significant role in determining life expectancy. Early-stage osteosarcoma has a higher survival rate compared to advanced-stage cancer.
-
Age at Diagnosis: As mentioned earlier, the age of the patient at diagnosis can impact life expectancy. Younger patients tend to have better outcomes.
-
Response to Treatment: The effectiveness of treatment, including surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, can greatly influence life expectancy.
-
Genetic Factors: Certain genetic mutations may increase the risk of developing osteosarcoma and can affect life expectancy.
-
Comorbidities: The presence of other health conditions can complicate the treatment process and impact life expectancy.
Treatment Options
The treatment of osteosarcoma typically involves a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Here is a brief overview of each treatment modality:
-
Surgery: The primary goal of surgery is to remove the tumor and surrounding healthy tissue. This may involve amputation of the affected limb or joint in some cases.
-
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is used to kill cancer cells throughout the body. It is often administered before surgery to shrink the tumor and after surgery to prevent recurrence.
-
Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy is used to destroy cancer cells and shrink tumors. It is often used in conjunction with surgery and chemotherapy.
Supportive Care and Quality of Life
In addition to the primary treatment modalities, supportive care is an essential aspect of managing osteosarcoma. Supportive care aims to alleviate symptoms, improve quality of life, and address the emotional and psychological needs of patients and their families. Some common supportive care interventions include:
-
Pain management
-
Physical therapy
-
Nutritional counseling
-
Psychological support
Conclusion
Understanding the life expectancy of individuals with OMS disease is crucial for patients and their families. While the prognosis can vary widely, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can significantly improve outcomes. By staying informed and proactive, patients can take steps to optimize their chances of survival and maintain a high quality of life.
| Factor | Impact on Life Expectancy |
|---|
