Understanding the OMS Gartner Magic Quadrant: A Detailed Overview
When it comes to evaluating Order Management Systems (OMS), the Gartner Magic Quadrant is a go-to resource for businesses seeking to understand the market landscape and identify the best solutions for their needs. This article will delve into the intricacies of the Gartner Magic Quadrant for OMS, providing you with a comprehensive, multi-dimensional introduction.
What is the Gartner Magic Quadrant?
The Gartner Magic Quadrant is a graphical representation of a market’s competitive landscape and positions various providers within that market according to their ability to execute and completeness of vision. It is a valuable tool for businesses looking to make informed decisions about their technology investments.
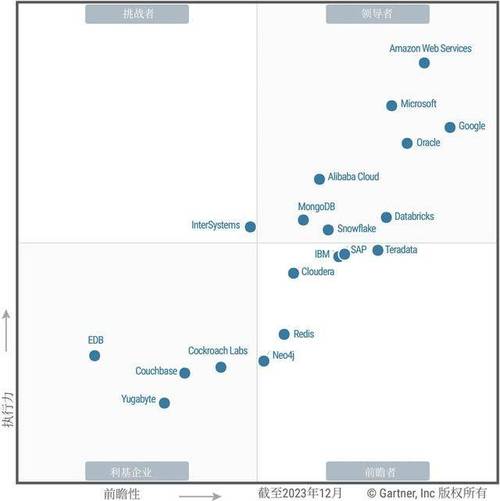
How is the OMS Gartner Magic Quadrant Structured?
The OMS Gartner Magic Quadrant is divided into four quadrants: Leaders, Challengers, Visionaries, and Niche Players. Each quadrant represents a different level of market presence and strategic direction.
| Quadrant | Description |
|---|---|
| Leaders | Leaders have a strong market presence and a clear vision for the future of OMS. They are often the preferred choice for businesses looking for a comprehensive solution. |
| Challengers | Challengers have a strong market presence but may lack a clear vision for the future. They are often seen as a viable alternative to leaders. |
| Visionaries | Visionaries have a clear vision for the future of OMS but may not have a strong market presence. They are often innovative and can offer unique solutions. |
| Niche Players | Niche Players have a limited market presence and focus on specific segments of the OMS market. They may be a good choice for businesses with specific needs. |
Key Factors Considered in the OMS Gartner Magic Quadrant
The Gartner Magic Quadrant evaluates OMS providers based on several key factors, including:
- Market Presence: The size, growth, and geographic reach of the provider’s OMS offerings.
- Product/Service: The features, functionality, and ease of use of the provider’s OMS solution.
- Customer Experience: The provider’s track record in delivering high-quality customer service and support.
- Execution: The provider’s ability to deliver on its promises and meet customer expectations.
- Completeness of Vision: The provider’s strategic direction and future plans for OMS development.
How to Use the OMS Gartner Magic Quadrant
When using the Gartner Magic Quadrant for OMS, consider the following steps:
- Identify your business needs and priorities.
- Review the providers in the Leaders quadrant, as they are often the best choice for most businesses.
- Consider providers in the Challengers and Visionaries quadrants if your needs align with their strategic direction.
- Research providers in the Niche Players quadrant if you have specific requirements that only they can meet.
- Compare the providers based on the key factors mentioned above.
- Make an informed decision based on your research and priorities.
Benefits of Using the OMS Gartner Magic Quadrant
Using the Gartner Magic Quadrant for OMS can provide several benefits, including:
- Increased confidence in your decision-making process.
- Access to a wealth of information about the OMS market and its leading providers.
- Insights into the strategic direction and future plans of OMS providers.
- Enhanced ability to compare and contrast different OMS solutions.
Conclusion
The Gartner Magic Quadrant for OMS is a valuable resource for businesses looking to understand the market landscape and identify the best OMS solutions for their needs. By considering the key factors and using the quadrant effectively, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your business goals.
