Understanding OMS Rules: A Comprehensive Guide
Order Management Systems (OMS) are essential tools for businesses looking to streamline their order processing and fulfillment. OMS rules are the backbone of these systems, ensuring that every order is handled efficiently and accurately. In this detailed guide, we will explore the various aspects of OMS rules, their importance, and how they can benefit your business.
What are OMS Rules?
OMS rules are a set of predefined guidelines and conditions that dictate how orders are processed within an OMS. These rules can be simple or complex, depending on the specific needs of your business. They help automate various tasks, such as order validation, inventory management, and shipping.
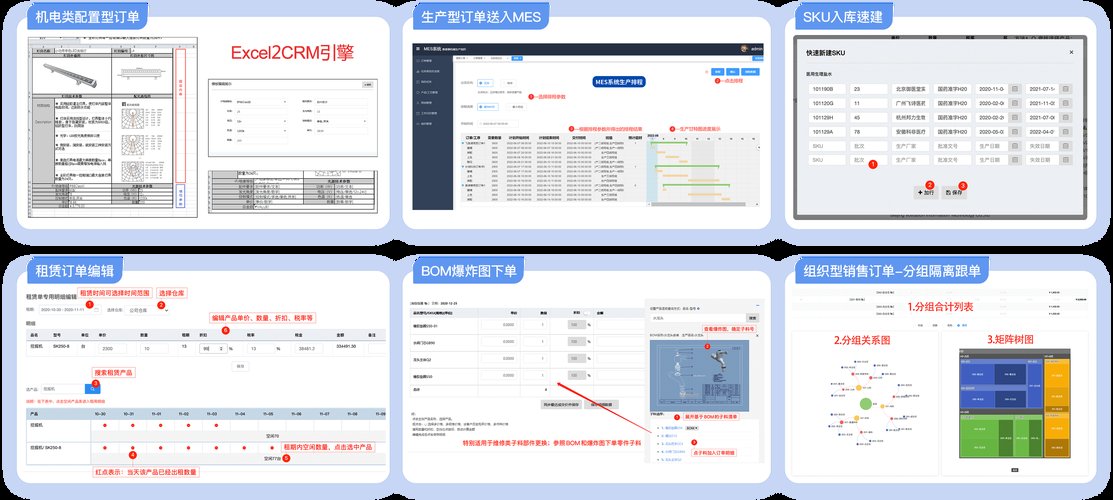
Here are some common types of OMS rules:
- Order Validation Rules: These rules ensure that orders meet specific criteria before they are processed. For example, you might have a rule that requires all orders to have a valid customer ID.
- Inventory Management Rules: These rules help manage your inventory levels by automatically updating stock quantities when orders are placed or fulfilled.
- Shipping Rules: These rules determine how orders are shipped, including selecting the appropriate shipping method, calculating shipping costs, and generating shipping labels.
- Pricing Rules: These rules manage pricing for products and services, including discounts, promotions, and special pricing for bulk orders.
Importance of OMS Rules
OMS rules play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of your business. Here are some key reasons why they are important:
- Increased Efficiency: By automating various tasks, OMS rules help reduce manual effort and save time, allowing your team to focus on more critical tasks.
- Improved Accuracy: OMS rules help minimize errors in order processing, ensuring that customers receive the correct products and services.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: By providing timely and accurate order fulfillment, OMS rules contribute to a positive customer experience.
- Cost Reduction: By streamlining operations and reducing errors, OMS rules can help lower your business costs.
Creating Effective OMS Rules
Creating effective OMS rules requires a thorough understanding of your business processes and customer needs. Here are some tips for creating successful OMS rules:
- Identify Your Business Needs: Understand the specific challenges and requirements of your business to determine which rules are necessary.
- Analyze Your Data: Review your historical data to identify patterns and trends that can inform your rule creation.
- Involve Stakeholders: Collaborate with various departments, such as sales, customer service, and logistics, to ensure that your rules align with their needs.
- Test and Refine: Test your rules in a controlled environment before implementing them in your live system. Continuously refine your rules based on feedback and performance data.
OMS Rules in Action
Let’s take a look at a few examples of how OMS rules can be implemented in a real-world scenario:
Example 1: Order Validation Rules
Suppose you have a rule that requires all orders to have a valid customer ID. When a new order is placed, the OMS checks if the customer ID is present and valid. If not, the order is flagged for review, and the customer is notified to provide the necessary information.
Example 2: Inventory Management Rules
Let’s say you have a rule that automatically adjusts your inventory levels when an order is placed. When a customer buys a product, the OMS deducts the quantity from the available stock, ensuring that you never oversell a product.
Example 3: Shipping Rules
Consider a rule that selects the fastest shipping method for orders placed before a certain time of day. This ensures that customers receive their orders as quickly as possible, improving their satisfaction.
Conclusion
OMS rules are a vital component of any successful order management system. By understanding the various types of rules and their importance, you can create a customized set of rules that will help streamline your business operations, improve customer satisfaction, and reduce costs. Remember to involve stakeholders, test your rules, and continuously refine them to ensure they meet your evolving business needs.
